Data Driven Plasma Modeling and Control
Introduction
Achieving a high-performance and stable tokamak plasma in a steady-state operation is a critical challenge for fusion reactors. However, human trials in experiments alone are not effective in finding the optimal operating condition to achieve a high-performance plasma, due to the presence of several competing objectives such as operation limits and various instabilities. Reinforcement learning, a dynamic decision-making method in machine learning, offers a promising approach to discovering the optimal trajectory for high-performance plasma since it can provide a powerful framework for control engineering by adaptive, data-driven, and model-free methods without a priori knowledge or a precise mathematical model of the system being controlled.
Previous studies have explored feedforward beta control with a KSTAR simulator based on LSTM and plasma shape control using the MPO algorithm. Moreover, Multiple 0D parameters control also has been conducted to control several physical parameters into different target values simultaneously with summing the reward function for each controlled parameter. However, since each physical parameter depends on different dynamics and constraints, there would be a Pareto optimal case where other solutions can simultaneously improve all objectives without worsening at least one of them. This means that it is reasonable to approach multiple 0D parameters control as a multi-objective problem where the presence of several competing objectives should be considered.
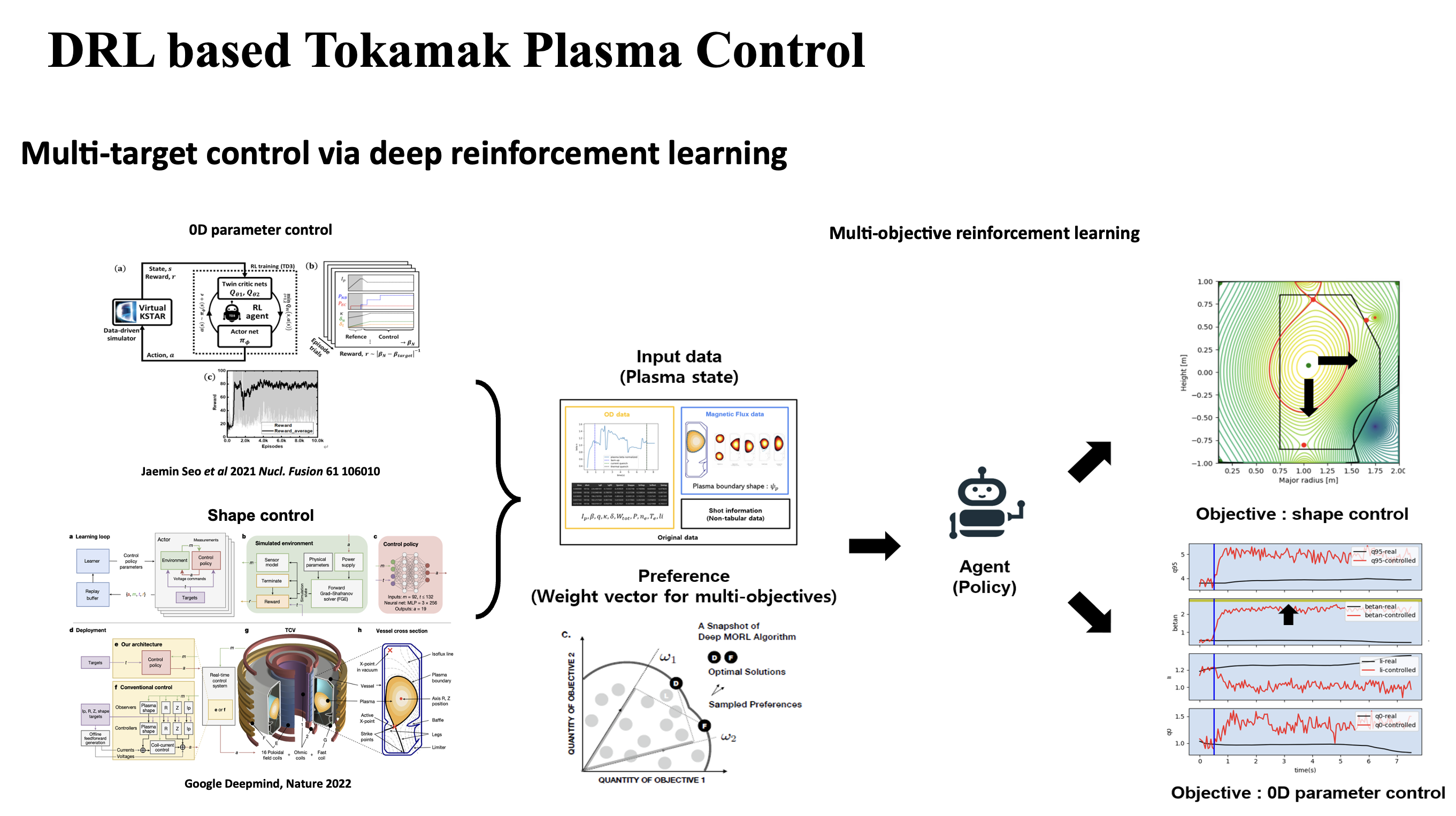
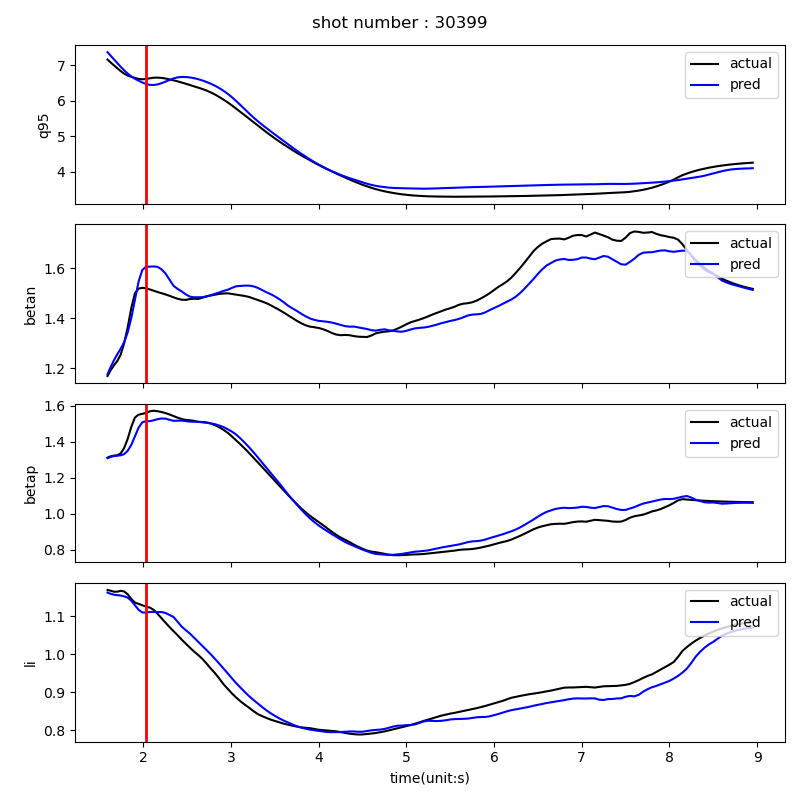
In this work, we develop the virtual KSTAR environment based on Transformer for approximating the state of the plasma in response to the control by RL agent. The above figure describes the overview of our work, aiming for multi-target control via multi-objective reinforcement learning combined with data-driven plasma simulator. Heating sources including NBI and EC heating, shape parameters, plasma current, and toroidal magnetic field are set as control variables. The targets are EFIT parameters. As a result, we demonstrate that the single agent can find the optimal policy that controls poloidal beta and safety factor to reach the target values simultaneously by multi-objective reinforcement learning.
Data-driven Tokamak Plasma Simulator
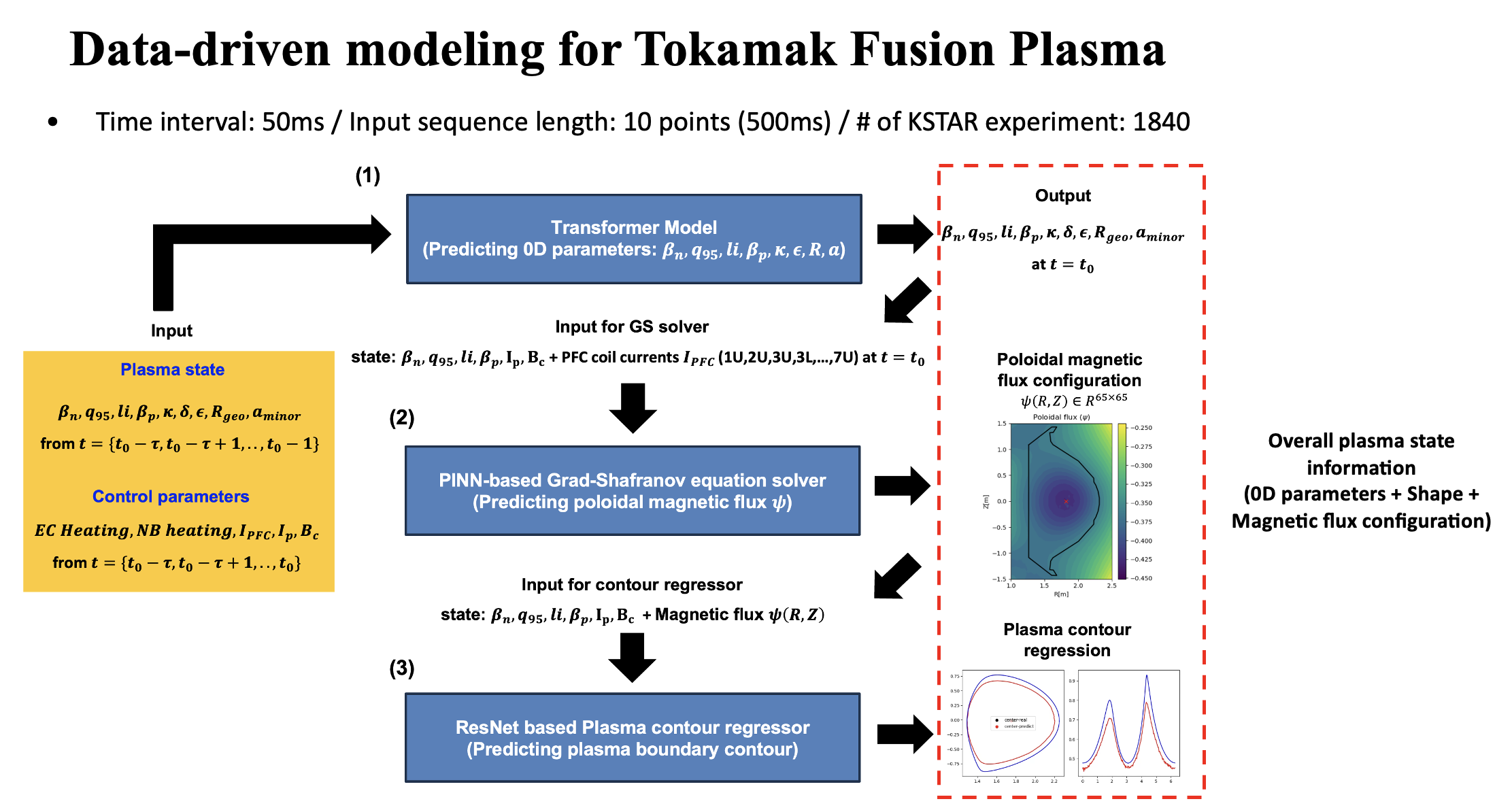
Our data-driven simulator consists of (1) time-integration model for estimating the next 0D parameters based on Transformer, (2) PINN-based Grad-Shafranov equation solver for computing magnetic flux (3) Plasma boundary idenfication model. Multiple modules are employed to predict and reconstruct the plasma equilibrium for each step and given to the RL controller as the state information with response to change of control variables.
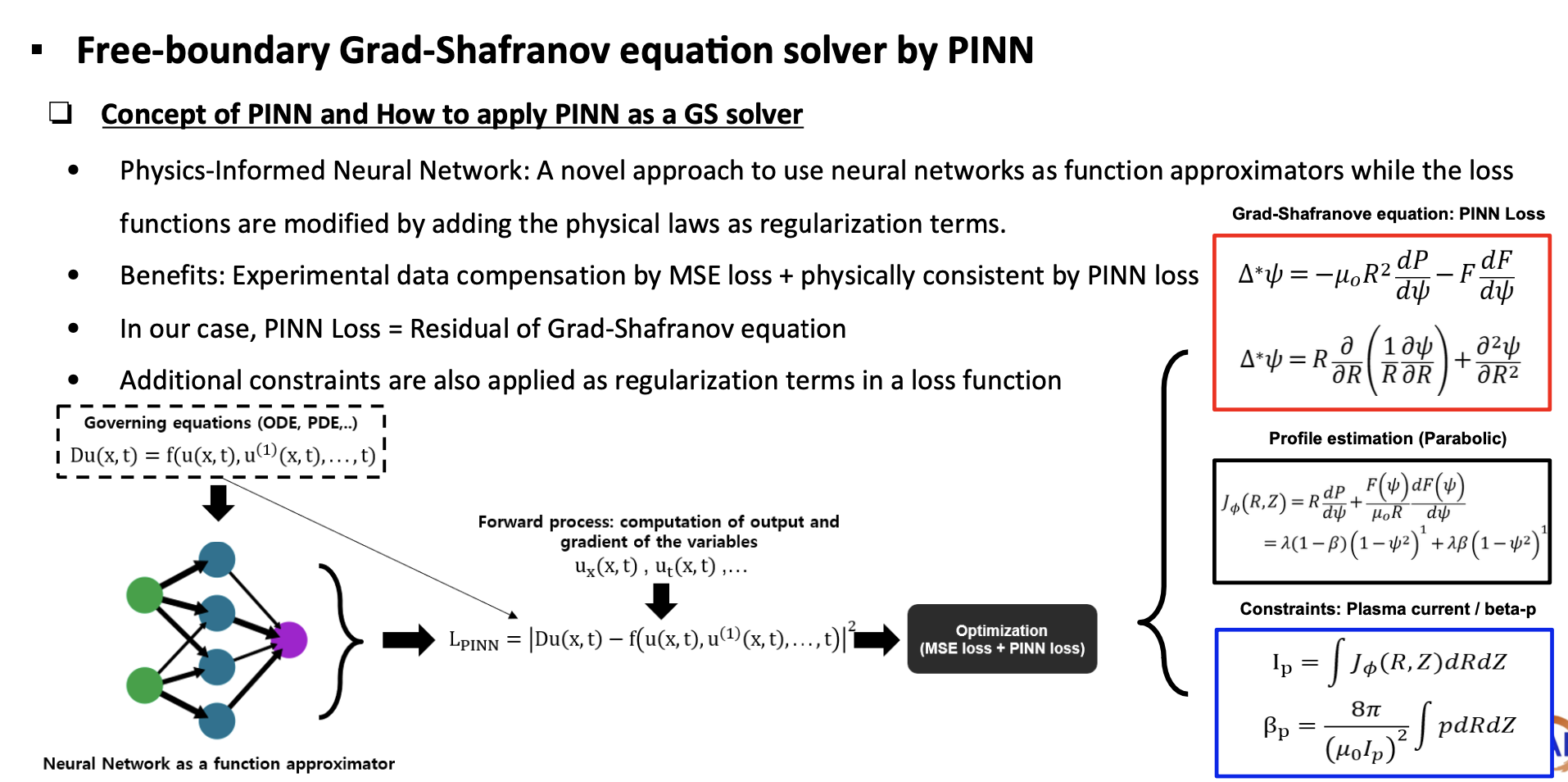
Here, the poloidal flux of the plasma is estimated by Grad-Shafranov solver based on Physics-Informed Neural Network (PINN). Not only the poloidal flux but also the profile of pressure and current can be estimated, allowing us to control advanced purpose including profile control in the future.
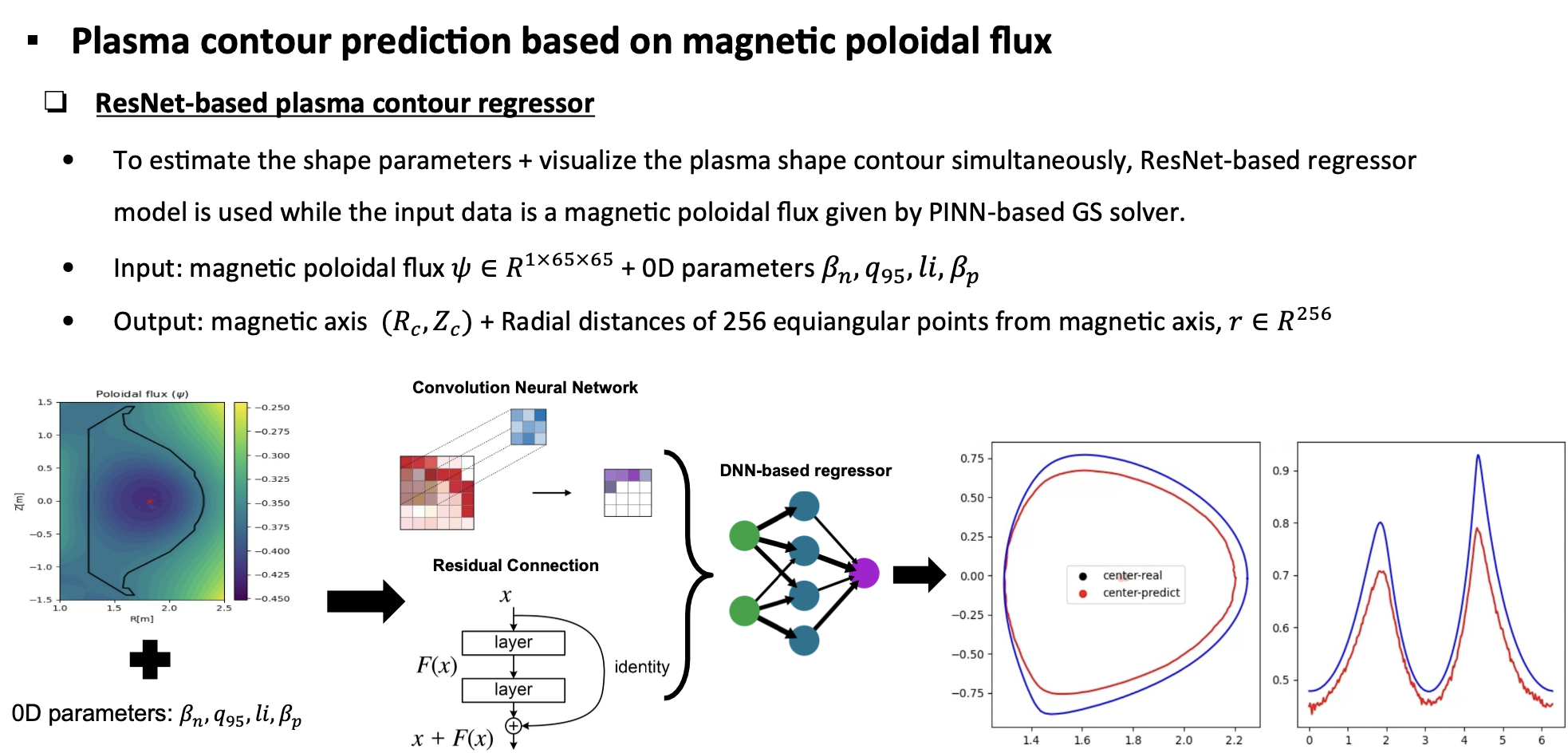
The boundary estimator is based on simple ResNet to visualize the boundary of the plasma and shows stable computation for capturing the boundary information compared with conventional methods.
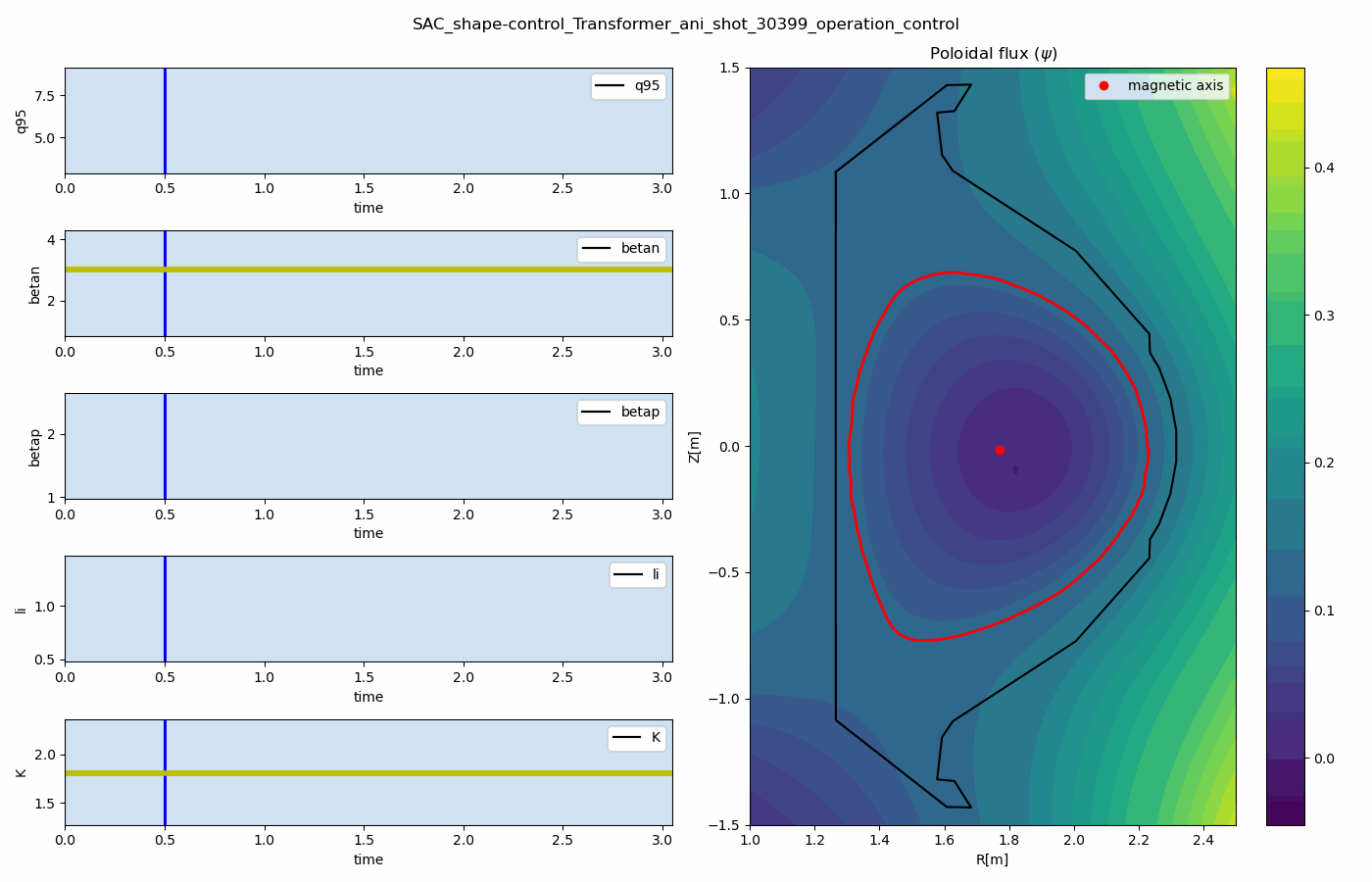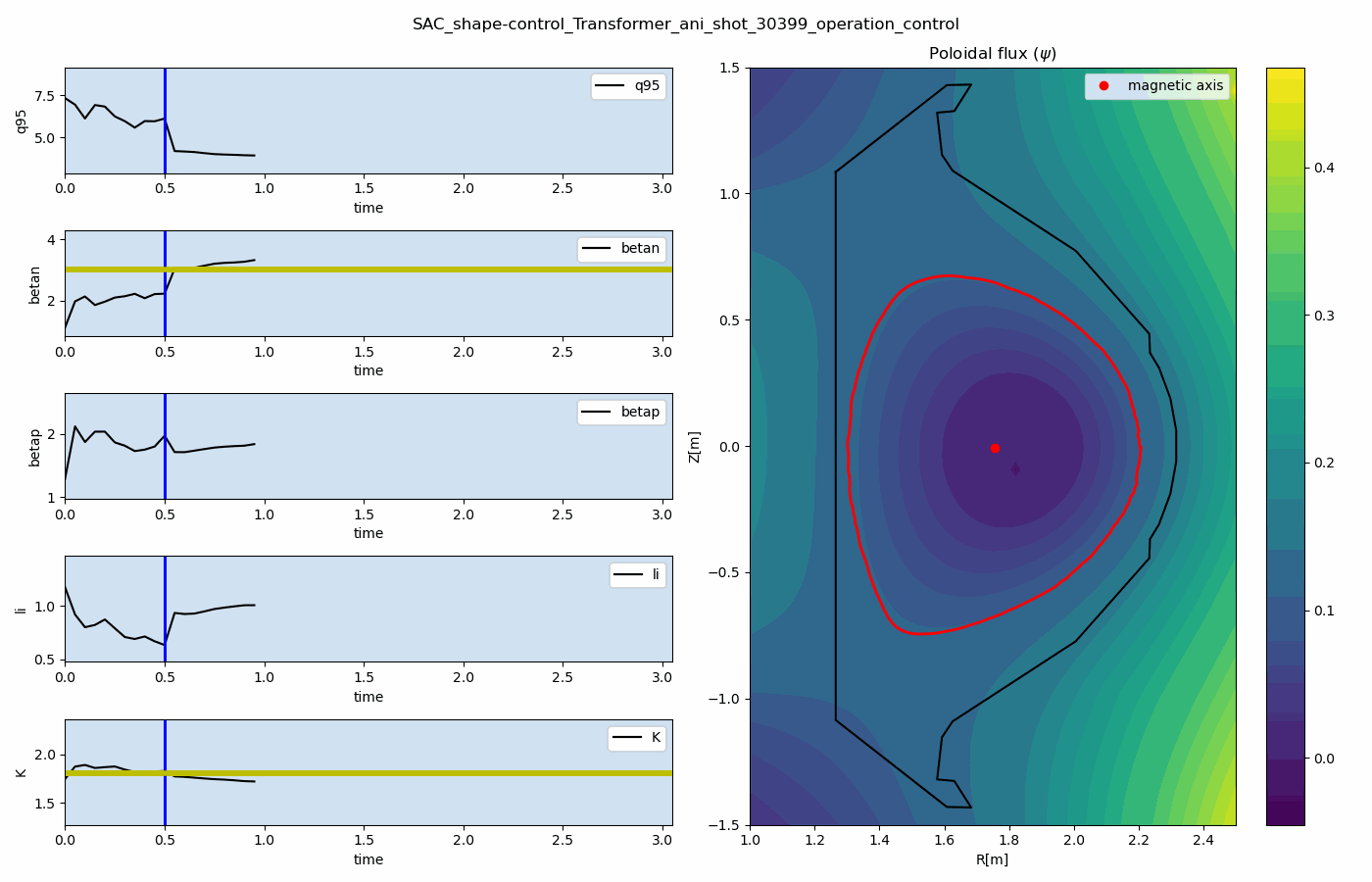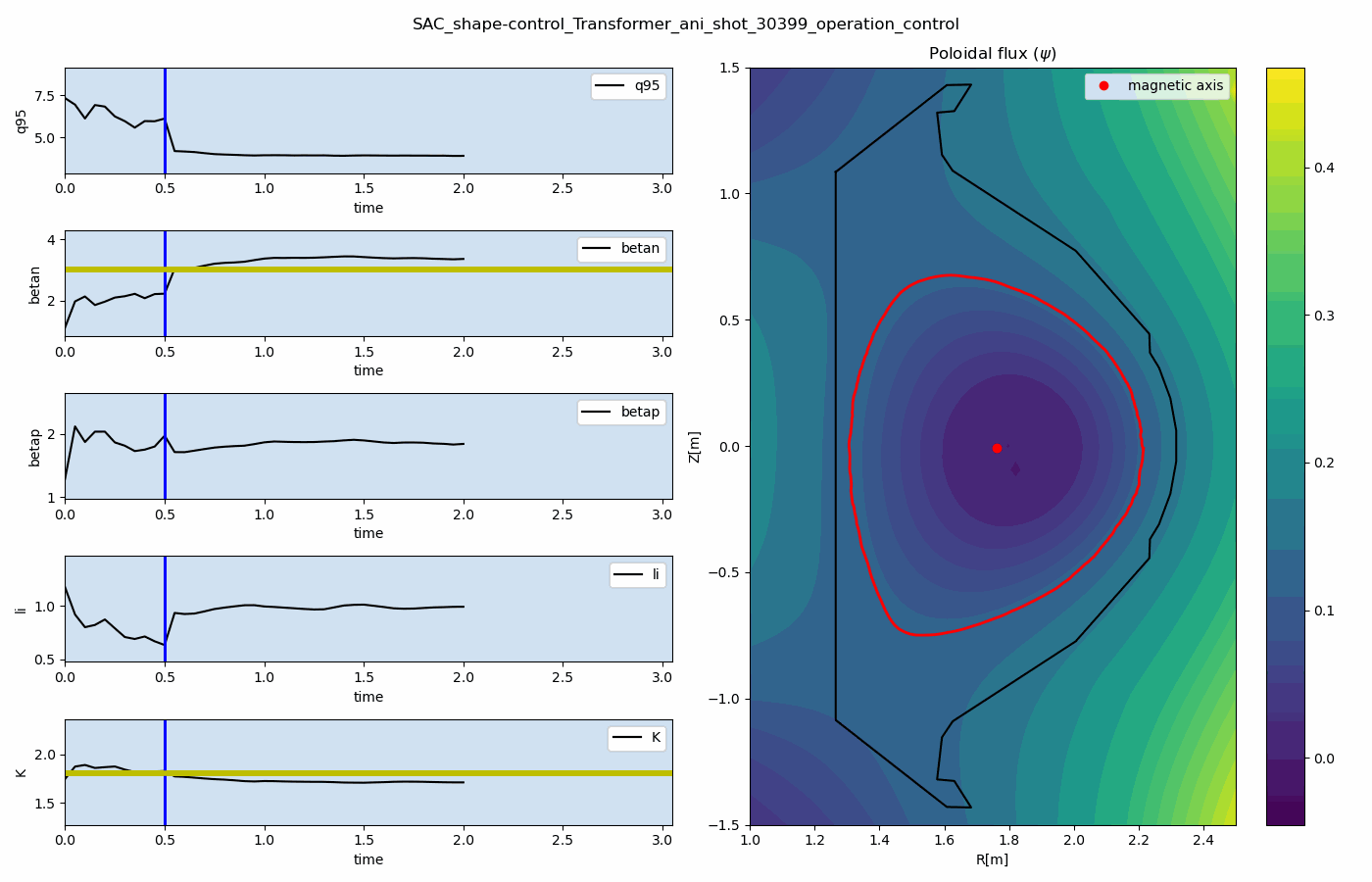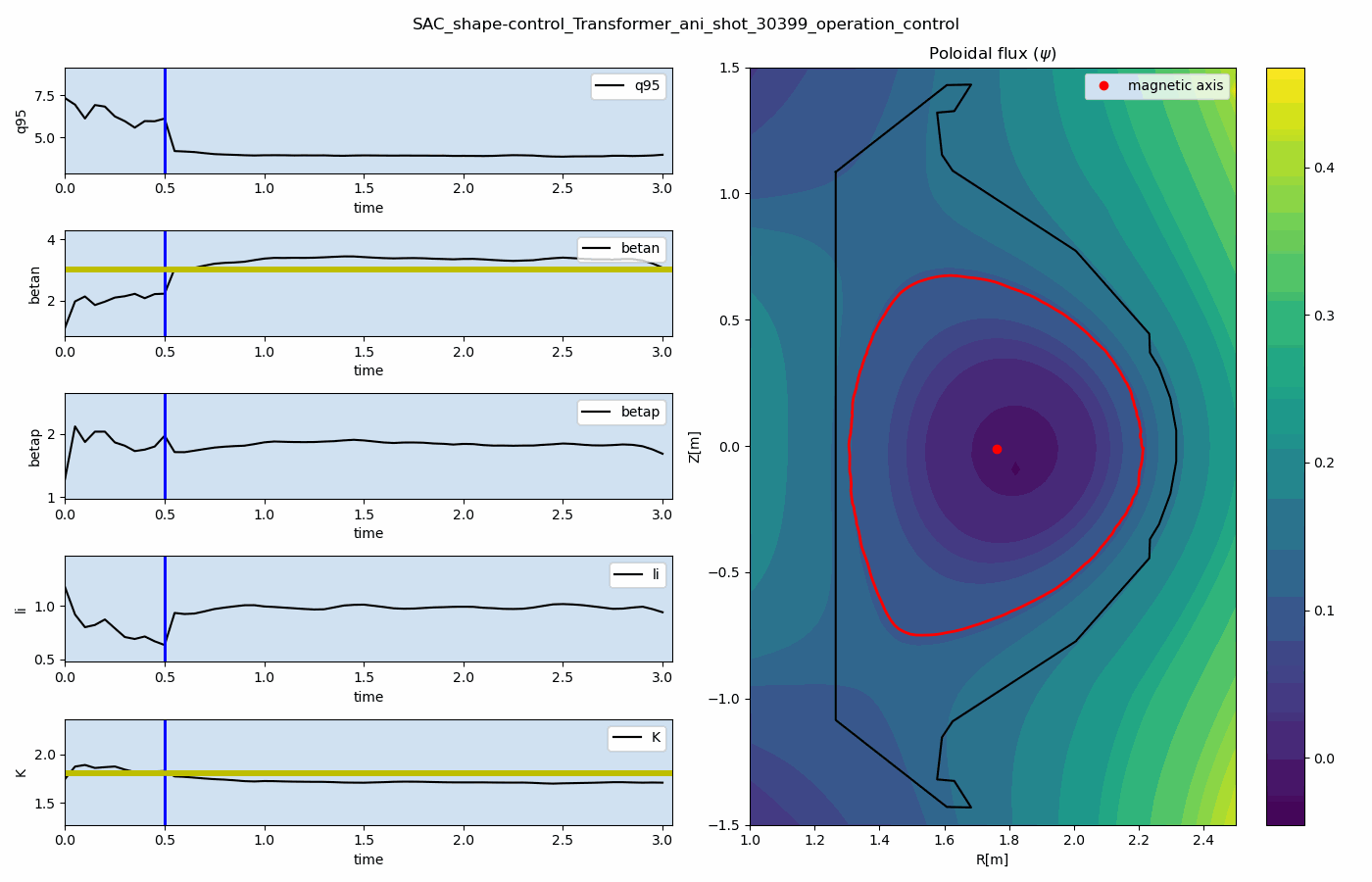
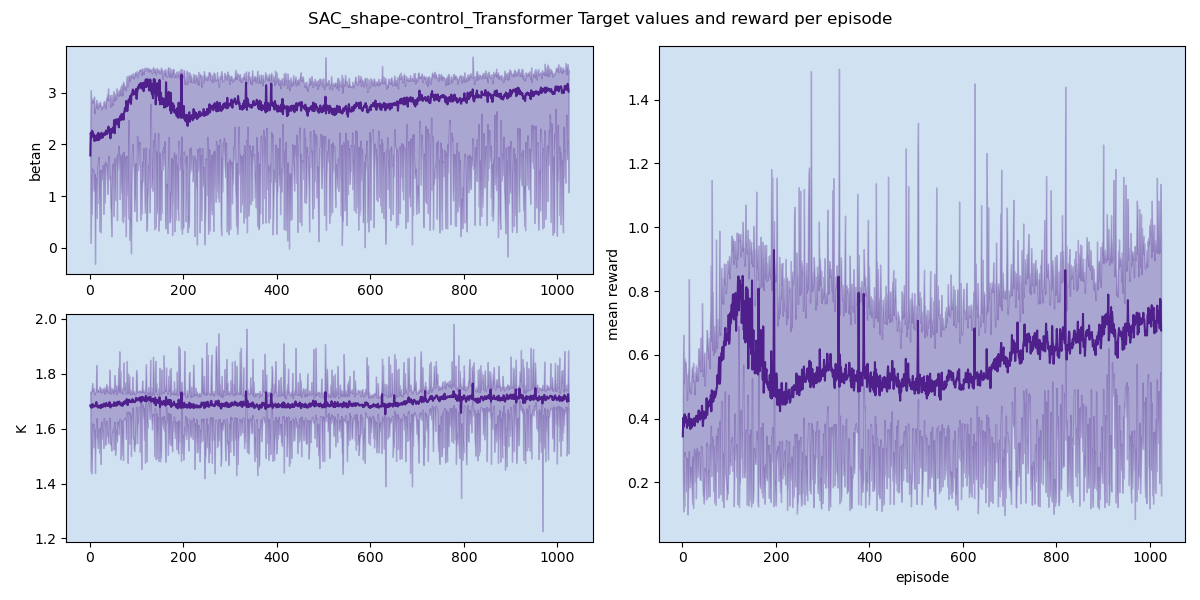
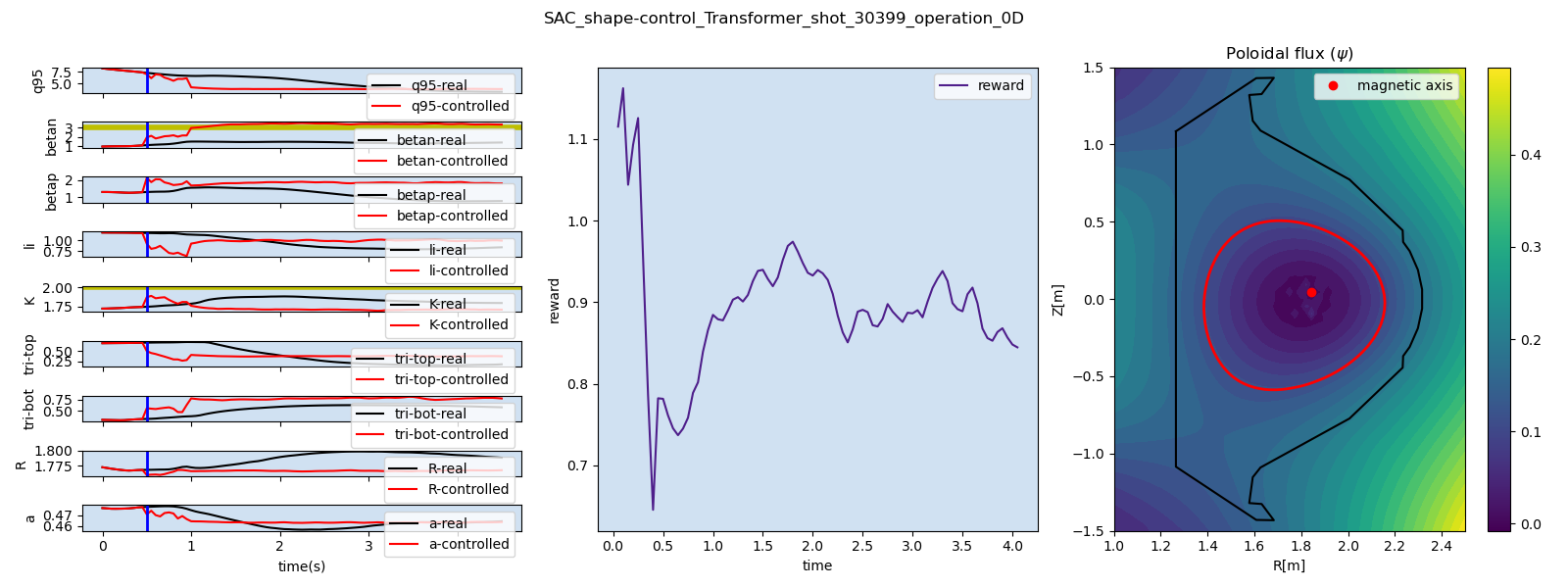
For multi-target control, we developed the multi-objectve reinforcement learning algorithm for multi-objective tokamak plasma operation control. The simulation results of plasma state prediction and control are given as below figures.
Article
Jinsu Kim. “Tokamak Plasma Operation Control using Multi-Objective Reinforcement Learning in KSTAR” International Fusion Plasma Conference 2023. Poster.
